pytorch 的实例的网络定义的时候给出了一个 CNN 的例子.
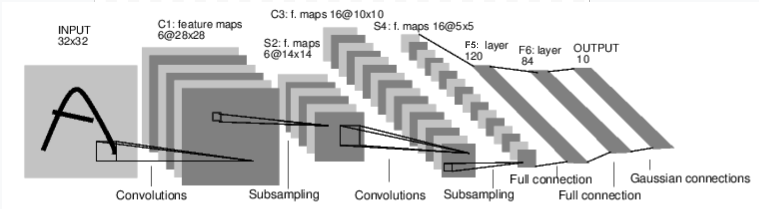
对应例子的代码如下.
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
def num_flat_features(self, x):
size = x.size()[1:]
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features
net = Net()
print(net)
'''
Net (
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear (400 -> 120)
(fc2): Linear (120 -> 84)
(fc3): Linear (84 -> 10)
)
'''
但是这模型如果直接用MNIST 28x28 的数据训练的话, 就存在数据size 不匹配的问题.
print( net.forward(Variable(torch.Tensor(1,1,28,28))).size())
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-3-5cc5395cfba7> in <module>()
40 print(net)
41
---> 42 print( net.forward(Variable(torch.Tensor(1,1,28,28))))
<ipython-input-3-5cc5395cfba7> in forward(self, x)
24 x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
25 x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
---> 26 x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
27 x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
28 x = self.fc3(x)
...
RuntimeError: size mismatch, m1: [1 x 256], m2: [400 x 120] at /Users/soumith/code/builder/wheel/pytorch-src/torch/lib/TH/generic/THTensorMath.c:1237
为什么会出现数据的 size 不对呢? 因为在网络的 __init__ 函数中只定义了一些主要的 layer;而且一些其他 layer 比如 max_pool2d 是在 Net.forward 中才引入; 而且经过 max_pool2d 之后数据的 size 会出现变化的. 这样带来问题就是有些数据的 size 会在两个地方影响. 违反了 SSOT 原则.
还有一个问题就是在 forward 函数中的重复重复代码; 这也是代码采用命令式方式来计算带来的问题.
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
那如何解决呢? 利用 nn.Sequential 串联各个层; 然后尽量减少不去使用 torch.nn.functional 中命令式的函数.
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5)
# 使用 Sequential 直接串联上各个层级
self.cnn1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d((2,2))
)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
# 调用更加简洁
x = self.cnn1(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
同样的方法把能串联的层级都串联起来
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.cnn = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d((2,2)),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.fullyConnections = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Linear(84, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cnn(x)
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = self.fullyConnections(x)
return x
那代码简洁了很多,而且对网络的定义也清晰很多, 但是 x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x)) 怎么办呢
# 创建一个 FeatureFlaten 的层级
class FeatureFlaten(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(FeatureFlaten, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
return x
def num_flat_features(self, x):
size = x.size()[1:] # all dimensions except the batch dimension
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features
def __repr__(self):
return 'FeatureFlaten()'
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.cnn = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d((2,2)),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
FeatureFlaten(), // 替换原来的 flat 函数
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Linear(84, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.cnn(x)
那接下来我们要解决 size 不匹配的问题了. 如果在最开始 Net 的 forward 函数的话, 直接用 print(x.size()) 的方式就可以了. 但是现在的网络采用这种申明式的方式就要采用另外的方式了.
# 定义 VariableSizeInspector 网络层
class VariableSizeInspector(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(VariableSizeInspector, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x):
print('after',type(x.creator) , x.size())
return x
def __repr__(self):
return 'VariableSizeInspector()'
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.cnn = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d((2,2)),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
VariableSizeInspector(), // 查看池化后的变量 size
FeatureFlaten(),
VariableSizeInspector(), // 查看平坦化后的变量 size
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Linear(84, 10)
)
Net (
(cnn): Sequential (
(0): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU ()
(2): MaxPool2d (size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2), dilation=(1, 1))
(3): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(4): ReLU ()
(5): MaxPool2d (size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2), dilation=(1, 1))
(6): VariableSizeInspector()
(7): FeatureFlaten()
(8): VariableSizeInspector()
(9): Linear (400 -> 120)
(10): Linear (120 -> 84)
(11): Linear (84 -> 10)
)
)
('after', <class 'torch.nn._functions.thnn.pooling.MaxPool2d'>, torch.Size([1, 16, 4, 4]))
('after', <class 'torch.autograd._functions.tensor.View'>, torch.Size([1, 256]))
通过日志就能发现输入变成 28x28 之后, 进入到全连接网络之前的 size 变成256, 所以 Sequential 的第9层的输入将400变为256就能使用 MNIST 的数据集了.
完
希望大家喜欢.
